The pandemic experience in Asia Pacific continues to be both distinct and diverse across the region. While contexts like India, Malaysia, and parts of Australia, press on through chronic lockdowns, or Movement Control Orders (MCOs), organizations in countries like China have been fully back for almost a year. As much as diverse experiences remain characterizing features in the region, so too does a desire to return to work places. As people begin to come back, it can be human nature to slip back into old patterns. But when it comes to the workplace, people will continue to expect a greater emphasis on safety — citing air quality and adherence to safety protocols as top needs. While safety measures (like fire suppression) have always been important in the office, the pandemic has highlighted the need for the office to play a role in mitigating the spread of disease and it has taught us a more holistic approach is required going forward.
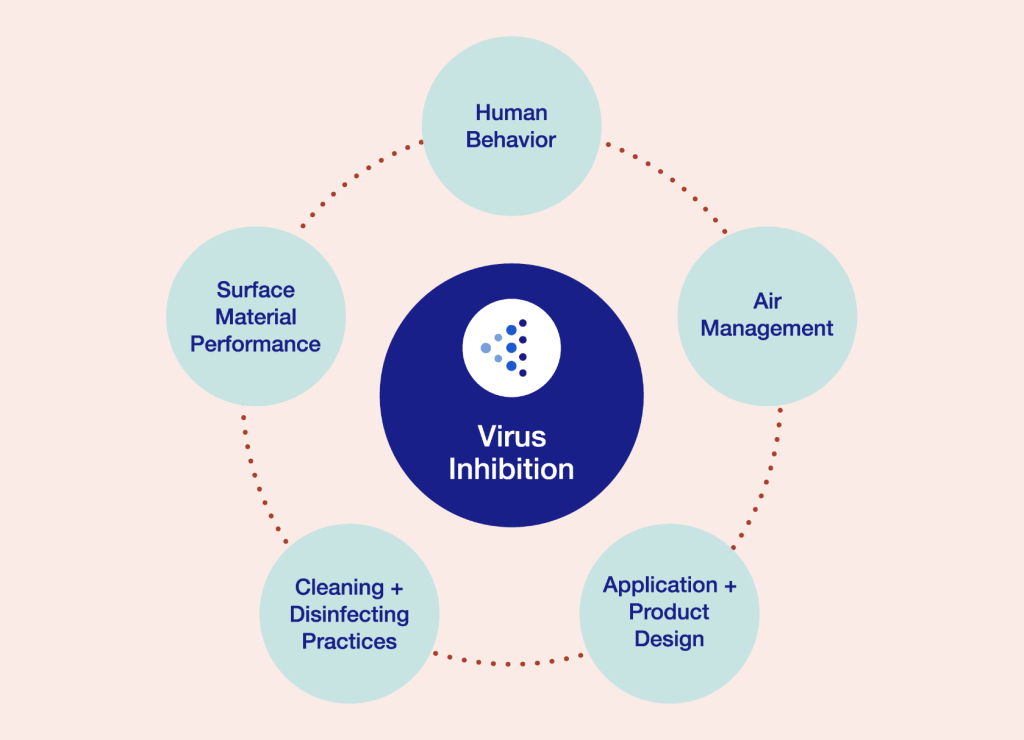
Creating a Safer Workplace
Steelcase consulted with leaders in workplace and product design, top-tier academic researchers and scientists who study airborne virus transmission, surface materials experts and studied data analytics-enabled experiences to inform a multi-faceted approach to workplace health and safety. The resulting framework (see above) focuses on five areas that can layer together to help create a safer environment – not only during the pandemic but during annual outbreaks like flu season, which can cost companies around the world billions of dollars in sick days and lost productivity.
New Health + Safety Priorities
73% Air quality
73% Adherence to safety protocols
72% Facility cleanliness
71% Physical distancing + boundaries
69% Density
66% Visitor protocols
59% Food and beverage safety
Steelcase Work Experience Diagnostic Study, September 2020
Dr. Lydia Bourouiba, MIT professor and director of The Fluid Dynamics Disease Transmission Laboratory, is collaborating with Steelcase to study disease transmission in the workplace. She notes in The BMJ that a comprehensive approach around people, air, surface and space is needed to minimize the risk of exposure and transmission while maximizing presence and space usage.
Human Behavior
Around the region, governmental health arms such as the Centre for Health Protection, Hong Kong, and the Ministry of Health Malaysia, have been releasing similar guidelines aimed at helping employers prevent the spread of COVID-19 in workplaces. Many guidelines recommend a number of key elements to mitigating the disease including behavior changes. Making vaccines available at no cost to eligible employees, healthy hygiene practices, staying home when sick, physical distancing and cloth face coverings for unvaccinated people are all suggested strategies.
New policies, protocols and expectations will encourage healthier behaviors and look different for each organization.
Despite a focus on airborne transmission of COVID-19, a commitment to hand washing and good hygiene does have long-term benefits, as OSHA suggests. There’s always a small risk of fomite (surface) transmission with any disease, and good hand hygiene will slow the spread of any illness including colds and flu.
Hand-washing stations and access to cleaning supplies will act as visual cues to remind people to commit to these healthier habits.
Contact tracing protocols, health screening questionnaires and temperature checks can add a layer of accountability for some organizations. Asking people to stay home when they feel sick and to watch for any signs of illness will also be important.
Transparency and visibility to these changes in behaviors is key. People want to know their organization is doing everything it can to keep them safe, and that includes ensuring people adhere to existing and updated safety protocols.
Air Management
With findings that aerosol transmission is primarily what’s spreading this coronavirus (as well as other viruses like influenza A, SARS and viral meningitis, among others), air management is a key area of focus when it comes to creating a safer workplace. After surveying more than 32,000 people in 11 countries, Steelcase found it was one of employees’ top safety concerns. Attention to air quality will not only help mitigate the spread of COVID-19 and other airborne diseases such as flu, but also impact other areas of wellness and address contamination caused by wildfires, smog and allergens.
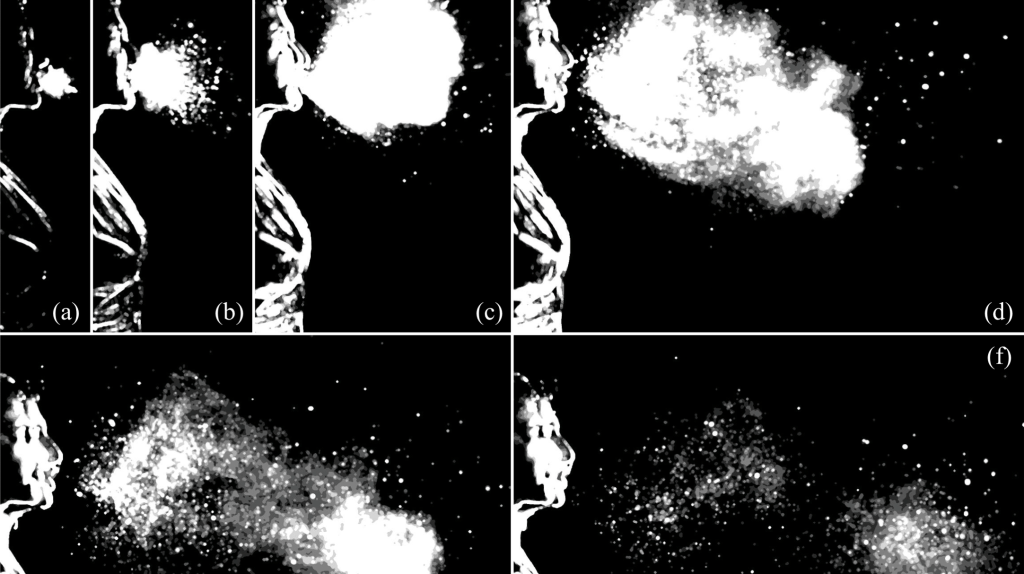
Courtesy: Bourouiba Research Group
Temperature, humidity level, and exchange and flow of air all contribute to a healthy environment. Companies planning new spaces, or who have control over their mechanical systems, can work with HVAC experts on implementing the latest guidance to help limit airborne spread and create healthier workplaces. For example, adding fans to windows to blow in outside air can increase ventilation.
But what if you can’t adjust your HVAC systems, or you want additional mitigation? Decreasing density in the space and adhering to appropriate distancing gives some expelled droplets a chance to fall to the ground before reaching anyone.
Research published by a leading biotechnology authority, the National Center for Biotechnology Innovation has also found “high-efficiency filters, stand-alone air cleaners and ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) units installed in rooms or ducts can be used to provide the equivalent of outdoor air supply to rooms,” which reduces the concentration of pathogens in the air. ASHRAE, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, agrees: “For locations that can’t upgrade the HVAC filter or increase outdoor air … in-room units are recommended to add cleaning capability.”
Portable air filtration products are available at a variety of scales, from room-wide to individualized. Steelcase recently began working with Clean Rooms International, a global designer of effective cleanroom solutions including air-handling equipment, to apply these elements to the workplace. At the room level, for example, Guardiair™, a Steelcase partner product by Clean Rooms International, has a cleanroom grade, IEST certified HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filter that removes particles as small as 0.3 microns, including respiratory droplets, with 99.99% efficiency. Off-the-shelf air filters tend to be designed to only capture dust and pet dander. On an individual level, Wynd® Personal Air Purifier uses a medical-grade filter to remove mold, bacteria and pollution, creating more comfortable personal spaces.
Application + Product Design
Designing for virus mitigation and safer spaces means considering how to balance new strategies:
Density – how many people are in a space, and which spaces need more attention based on usage.
Geometry – adjusting how furniture is configured to avoid face-to-face orientation and direct air flow to and from air purifiers and vents.**
Division – adding barriers, especially in places where distancing is not possible, to contain people’s exhalations.
Research tells us people want a safe workplace – but they also need it to be compelling and inspiring.
Collaboration is a key benefit and motivator for bringing people back to the office. Shared spaces can create the vibe people crave in the workplace and can be designed with infection-control measures in mind. Collaboration and social spaces can be situated in open areas to allow for air flow and flexibility in terms of meeting size. And since lounge furniture is freestanding, it can often easily be moved apart to accommodate distancing, placed at angles to change geometry, or shielded to create division.
Smart sensing-technology embedded throughout the workplace will help organizations use data to monitor occupancy and identify hotspots that might require more attention or additional adjustments. More hands-free technology like space scheduling devices or even automatic faucets and doors will add to a safer environment overall.
Surface Materials Performance
Soft surfaces contribute to a welcoming aesthetic that can feel more like home, bridging the transition from working at home to being back in the office. And research is providing initial evidence that fabrics are effective at reducing the surface-to-surface transmission of coronavirus. The COVID-19 virus remains active on porous surfaces a much shorter time than non-porous surfaces like glass and metal, according to a study published in The Lancet Microbe.
Steelcase commissioned an independent lab to conduct the first-ever study of how long the virus remained active on contract surface materials. Using ISO 18184 and OC43 (an ASTM-recommended surrogate for SARS CoV-2), the lab found the following:
| After 2 hours |  |
no active virus was recovered from the polyurethane-coated fabric. |
| After 12 hours |  |
no active virus was recovered from the 100% polyester fabric. |
| At the 24 hour point |  |
the amount of active virus that could be recovered from the 100% wool fabric was reduced by 93.6%. |

In other words, almost no virus was detectable on the three fabrics within a day. Other enveloped viruses such as influenza A have been shown to display similar differential survival times on porous vs. non-porous materials, further supporting the contention that textiles are likely not a predominant source of contact transmission during annual flu outbreaks (as with SARS-CoV-2).
Disinfection is still important if there’s been a suspected case of COVID-19, flu or other illness within the last 24 hours. But typically, routine cleaning should be sufficient to lower transmission risk.
Materials that have virus or bacteria-inhibiting properties can add another layer of protection. Copper, for example, has long been known to have antimicrobial properties. And there’s strong research showing copper can be an effective countermeasure against SARS-CoV-2, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Investing in copper for high-touch, multi-use areas like door handles can support cleaning protocols by ensuring the virus doesn’t live long on surfaces between cleanings.
Cleaning + Disinfecting Practices
There are three main factors to consider when thinking about mitigating surface transmission of viruses and bacteria in the workplace:
– How many people use the space on a daily basis?
– How often is a surface touched?
– How often will a space be cleaned?
When considering these three factors together, organizations can focus on high-touch, multi-use surfaces that carry the most risk — like conference room table surfaces, meeting room door handles and conference chair arms. Low-touch surfaces like chair seats and bases, monitors, walls, floors and table legs carry a much lower risk of transmission.
More frequent and visible cleaning – especially of high-traffic areas – can help people feel at ease. And disinfection is recommended when there has been a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 within the last 24 hours.
“Clean surfaces regularly with standard disinfectants.”
WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION (WHO)
Yet, scientists caution against “hygiene theater” – or overcleaning . Overuse of disinfectants and antimicrobial products can lead to superbugs and trigger health and environmental issues.
Thinking Long Term
Safety is essential as people return to a better work experience than the one they left. People want to both be safe and feel safe – which means new safety measures and protocols that they can not only see, but also trust are being put into practice. A systemic, multi-faceted approach that includes attention to human behavior, air management, application and product design, surface materials, and cleaning and disinfecting practices considers the coronavirus today, but is also applicable to colds, seasonal flu and indoor allergies as well. The goal is to create a workplace that’s comfortable for all employees and ready to respond as conditions change.
Sources:
*Steelcase Global Return to Workplace March 2021
** Healthy Teaching Recommendations, Prof. Lydia Bourouiba, MIT, August 2020




